04. Remediation Planning Fundamentals
Remediation Planning Fundamentals
ND545 C3 L3 A04 Remediation Planning Fundamentals Part 1 V3
Overview
The purpose of security testing is to find security gaps. To prevent attackers from exploiting those, they now have to be fixed. Remediation planning helps security professionals understand and prioritize which vulnerabilities matter most. This process of fixing gaps is a foundational part of the overall vulnerability management process.
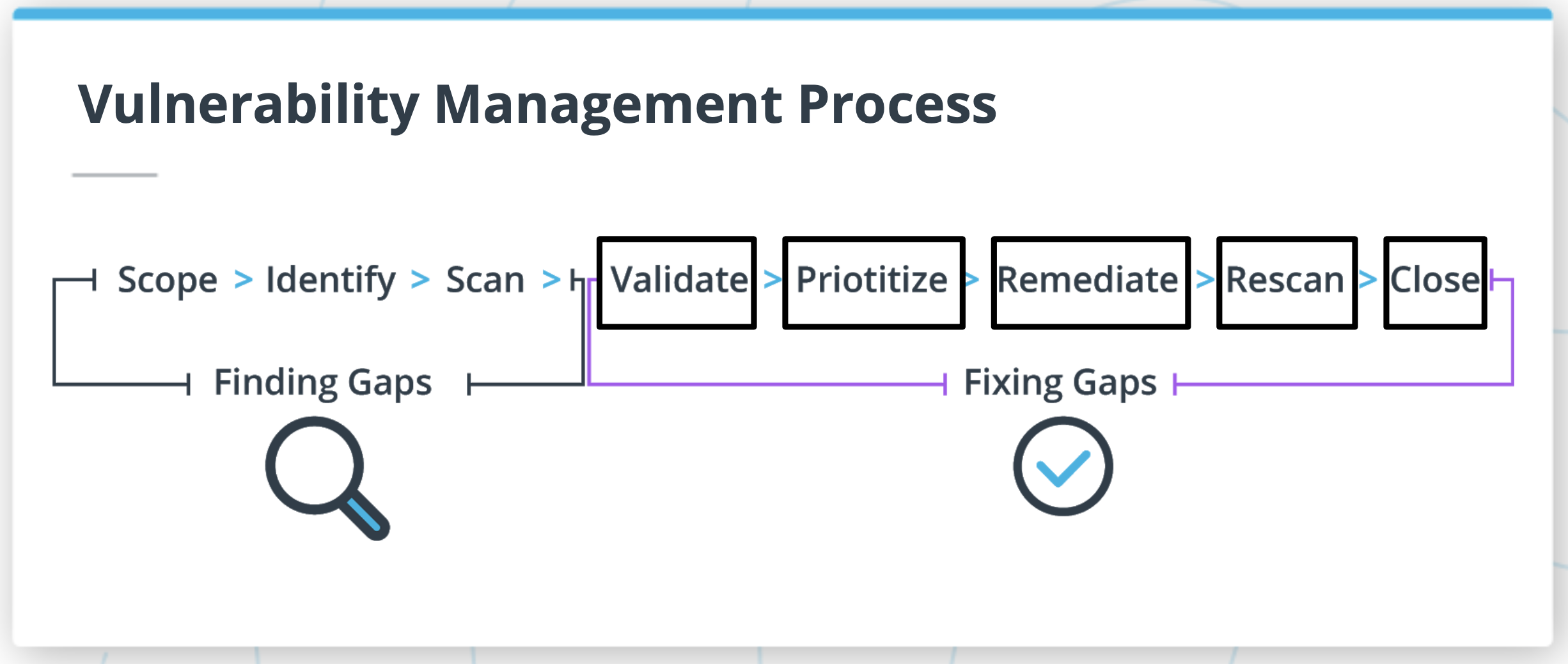
The vulnerability remediation process includes five main steps:
- Validate: Confirm that vulnerabilities are valid and remove any false positives.
- Prioritize: Rank vulnerabilities based on risk and other factors that help signify what should be addressed first.
- Remediate: Work with appropriate resources to fix the issues.
- Retest: Rescan or retest to confirm that the vulnerability has been fixed, and that other gaps were not exposed in the process.
- Close: Document the closure of the vulnerability.
Understanding Vulnerabilities
A core concept used to discuss and characterize vulnerabilities is the severity. Ratings are based on significance of vulnerability and common severity levels are Critical, High, Medium, and Low.
Because there are so many vulnerabilities spread across various systems, there needed to be a common scoring convention and way to measure severity. Without a standard, the same vulnerability could be defined as critical in one place, while it’s medium severity in another place. CVSS was created to address this.
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) provides a consistent way to score findings that can then be translated into a qualitative rating such as low, medium, high, and critical. This can help companies accurately evaluate and prioritize findings within their vulnerability management processes.
Scoring consists of three metric groups
Base – access vector, access complexity, impact to CIA, etc.
Temporal – exploitability, available remediation measure, vuln report confidence
Environmental – collateral damage, target distribution, CIA impact
Learn more by reviewing the user guide: https://www.first.org/cvss/user-guide, the FAQ https://www.first.org/cvss/v2/faq, and the calculator https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln-metrics/cvss/v3-calculator
ND545 C3 L3 A04 Remediation Planning Fundamentals Part 2
The point of CVSS scoring is to have a standardized way to qualify vulnerability severity levels. However, scanning tools and security vendors also often come up with their own custom ratings as well, which may be different from CVSS. While CVSS scoring is the most common and recommended standard, sometimes companies opt to stick with their own ratings or the ratings of a different vendor. For example, if you are conducting a scan using a tool that a vendor has developed, especially for your industry, you may choose to rely on the customized severity rating they use instead of the generic scoring provided through CVSS. There is no wrong answer; however, whichever route a company chooses, it’s important to remain consistent.